Professor

| Office: | BS 325 |
|---|---|
| Phone: | 410-455-2268 |
| Email: | wolf@umbc.edu |
Education
Postdoctoral in Molecular Genetics, Harvard Medical School, 1975;
Ph.D. in Microbiology, University of Cincinnati, 1970
M.S. in Microbiology, University of Cincinnati, 1968
B.A. in Psychology, University of Cincinnati, 1963
Professional Interests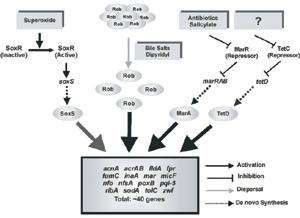
Like most faculty, my professional interests fall into three areas: research, teaching, and service. I get great pleasure from all of them. In research, I have long studied mechanisms of gene regulation in bacteria. During my initial years at UMBC, I worked on understanding growth rate-dependent regulation (GRDR) of central metabolism genes in E. coli. This form of regulation coordinates gene expression with the cellular growth rate as it is determined by the nutritional quality of the growth medium. The main gene we studied was gnd, which encodes 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase, an enzyme of the pentose phosphate pathway. We discovered that GRDR ofgnd is exerted at the level of translation initiation and involves the “internal complementary sequence” (ICS), a regulatory element lying deep within the gnd mRNA and whose sequence is complementary to the ribosome binding site (RBS) of the mRNA. Formation of a long-range secondary structure in the mRNA between the RBS and the ICS plays a key role in GRDR of gnd. We also studied GRDR of zwf, which encodes glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase.
Publications
Taliaferro, L.P.*, Keen* III, E.F., Alberola-Sanchez, N. & Wolf, R.E. 2012. Transcription activation by Escherichia coli Rob at class II promoters: protein-protein interactions between Rob’s N-terminal domain and the sigma 70 subunit of RNA polymerase. J. Mol. Biol. 419:139-157. doi:10.1016/j. jmb.2012.03.019. *These authors contributed equally to this work.
[Abstract] [Text]
Zafar, M.A., I.M. Shah and R.E. Wolf, Jr. 2010. Protein-protein interactions between sigma 70 region 4 of RNA polymerase and Escherichia coli SoxS, a transcription activator that functions by the prerecruitment mechanism: evidence for “off-DNA” and “on-DNA” interactions”. J. Mol. Biol. 401:13-32.
[Abstract]
Griffith, K.L., M.M. Fitzpatrick and R.E. Wolf, Jr. 2009. Two functions of the C-terminal domain of Escherichia coliRob: mediating “sequestration-dispersal” as a novel off-on switch for regulating Rob’s activity as a transcription activator and preventing degradation of Rob by Lon protease. J. Mol. Biol. 388:415-430.
[Abstract]
Shah, I.M. and R. E. Wolf, Jr. 2006. Sequence requirements for Lon-dependent degradation of the Escherichia colitranscription activator SoxS: identification of the SoxS residues critical to proteolysis and specific inhibition of in vitrodegradation by a peptide comprised of the N-terminal 21 amino acid residues. J. Mol. Biol., 357:718-731.
[Abstract]
[Abstract]
Griffith, K.L., S.M. Becker and R.E. Wolf, Jr. 2005. Characterization of TetD as a transcriptional activator of a subset of genes of the Escherichia coli SoxS/Mar/Rob regulons. Mol. Microbiol. 56:1103-1117. Erratum. Mol. Microbiol.57:306.
[Abstract]
Griffith, K.L. and R.E. Wolf, Jr. 2004. Genetic evidence for pre-recruitment as the mechanism of transcription activation by SoxS of Escherichia coli: the dominance of DNA binding mutations of SoxS. J. Mol. Biol. 344:1-10.
[Abstract]
Shah, I.M. and R.E. Wolf, Jr. 2004. Novel protein-protein interaction between Escherichia coli SoxS and the DNA binding determinant of the RNA polymerase α subunit: SoxS functions as a co-sigma factor and redeploys RNA polymerase from UP-element-containing promoters to SoxS-dependent promoters during oxidative stress. J. Mol. Biol. 343:513-532.
[Abstract]
Griffith, K .L., I.M. Shah, and R. E. Wolf, Jr. 2004. Proteolytic degradation of the Escherichia coli transcription activators SoxS and MarA as the mechanism for reversing the induction of the superoxide (SoxRS) and multiple antibiotic resistance (Mar) regulons. Mol. Microbiol. 51:1801-1816
[Abstract]
Griffith, K.L. and R.E. Wolf, Jr. (2002) A comprehensive alanine scanning mutagenesis of the Escherichia colitranscription activator SoxS: identifying amino acids important to DNA binding and transcription activation. J. Mol. Biol. 322:237-257.
[Abstract]
Griffith, K.L., I.M. Shah, T.E. Myers, M.C. O’Neill, and R.E. Wolf, Jr. (2002) Evidence for “pre-recruitment”as a new mechanism for transcription activation in Escherichia coli the large excess of SoxS binding sites per cell relative to the number of SoxS molecules per cell. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 91:979-986. Erratum. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 294:1191.
[Abstract]
Griffith, K.L. and R.E. Wolf, Jr. (2002) Measuring β-galatosidase activity in bacteria: cell growth permeabilization, and enzyme assays in 96-well arrays. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 290:397-402. Erratum. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 292:292.
[Abstract]
Griffith, K.L. and R.E. Wolf, Jr. (2001) Systematic mutagenesis of the DNA binding sites for SoxS in the Escherichia coli zwf and fpr promoters: identifying nucleotides required for DNA binding and transcription activation. Mol. Microbiol.40:1141-1154. Erratum. Mol. Microbiol. 42:571.
[Abstract]
Egan, S.M., A.J. Pease, J. Lang, X. Li, V. Rao, W.K. Gillette, R. Ruiz, J.L. Ramos, and R.E. Wolf, Jr. (2000) Transcription activation by a variety of AraC/XylS family activators does not depend on the class II-specific activation determinant in the N-terminal domain of the RNA polymerase alpha subunit. J. Bacteriol. 182:7075-7077.
[Abstract]
Wood, T.I., K.L. Griffith, W.P. Fawcett, K.-W. Jair, T.D. Schneider, and R.E. Wolf, Jr. 1999. Interdependence of the position and orientation of SoxS binding sites in the transcriptional activation of the Class I subset of Escherichia colisuperoxide-inducible promoters. Mol. Microbiol. 34:414-430.
[Abstract]
Lundberg, B.E., R.E. Wolf, Jr., M.C. Dinauer, Y.Xu, and F.C. Fang. 1999. Glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase is required for Salmonella typhimurium virulence and resistance to reactive oxygen and nitrogen intermediates. Infect. Immun. 67:436-438.
[Abstract]
Jair, K.-W., X.Yu, K. Skarstad, B.Thony, N. Fujita, A. Ishihama, and R. E. Wolf, Jr. 1996. Transcriptional activation of promoters of the superoxide and multiple antibiotic resistance regulons by Rob, a binding protein of the Escherichia coli origin of chromosomal replication. J. Bacteriol., 178:2507-2513.
[Abstract]
Martin, R.G., K.-W. Jair, R.E. Wolf, Jr., and J.L. Rosner. 1996. Autoactivation of the marRAB multiple antibiotic resistance operon by the MarA transcriptional activator in Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol.:178:2216-2223.
[Abstract]
Jair, K.W., W.P. Fawcett, N. Fujita, A. Ishihama, and R.E. Wolf, Jr. 1996. Amibdextrous transcriptional activation by SoxS: Requirement for the C-terminal domain of the RNA polymerasae alpha subunit in a subset of Escherichia colisuperoxide inducible genes. Mol. Microbiol., 19:307-317.
[Abstract]
Jair, K.-W., R.G. Martin, J.L. Rosner, N. Fujita, A. Ishihama, andR.E. Wolf, Jr. 1995. Purification and regulatory properties of MarA protein, a transcriptional activator of Escherichia coli multiple antibiotic resistance and superoxide resistance promoters. J. Bacteriol.177:7100- 7104.
[Abstract]
Fawcett, W.P., and R.E. Wolf, Jr. 1995. Genetic definition of the Escherichia coli zwf”soxbox”, the DNA binding site for SoxS-mediated induction of glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase in response to superoxide. J. Bacteriol.177:1742-1750.
[Abstract]
Chang, J.T. C. B.-R. Green, and R.E. Wolf, Jr. 1995. Inhibition of translation initiation on Escherichia coli gnd mRNA by formation of a long range secondary structure involving the ribosome binding site and the internal complementary sequence. J. Bacteriol.177:6560-6567.
[Abstract]
Fawcett, W.P., and R.E. Wolf, Jr. 1994. Purification of a MalE-SoxS fusion protein and identification of the control sites of Escherichia coli superoxide-inducible genes. Mol. Microbiol. 14:669-679.
[Abstract]
Courses Taught
